Data Types: Scalar, Vector, Matrix and Tensor
A scalar is a single number, a vector is a list of numbers, and a matrix is a grid of numbers arranged in rows and columns. These are fundamental building blocks in mathematics, physics, and computer science.
Scalars:
Represent single numerical values, like 7, -2.5, or π. Examples include temperature, mass, or a simple measurement.
Vectors:
Ordered lists of numbers, which can be represented as rows or columns. Can represent direction and magnitude (like velocity) or coordinates of a point in space. Examples include position in a 2D or 3D space (x, y, or x, y, z coordinates) or forces acting on an object.
Matrices:
Two-dimensional arrays of numbers, organized into rows and columns. Used to represent linear transformations, store data in a structured way, and perform various mathematical operations. Examples include tables of data, transformation matrices in computer graphics, and covariance matrices in statistics. In essence, scalars are the simplest, vectors are one-dimensional arrays, and matrices are two-dimensional arrays of numbers. They are building blocks for more complex mathematical structures like tensors.
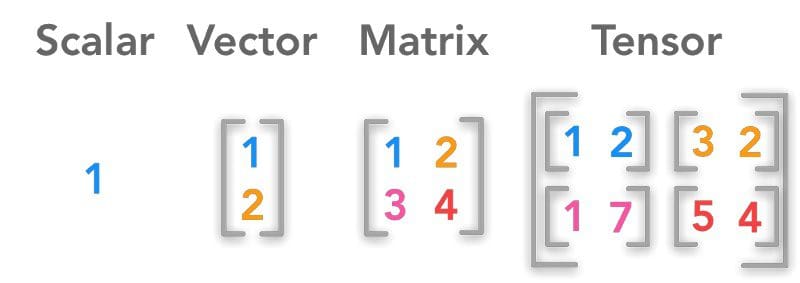
Tensors:
In essence, tensors are mathematical objects that generalize scalars, vectors, and matrices to higher dimensions. They are used to represent and manipulate data in various fields, including physics, mathematics, and computer science, particularly in areas like deep learning. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
- Generalization: Tensors can be thought of as containers that hold data in multiple dimensions, similar to how vectors are one-dimensional arrays and matrices are two-dimensional arrays. A scalar is a tensor of rank 0, a vector is a tensor of rank 1, and a matrix is a tensor of rank 2.
- Mathematical Definition: In mathematics, a tensor is a multilinear object that describes relationships between vectors, scalars, and other tensors. A tensor can be thought of as a function that takes vectors as input and produces a scalar, another vector, or another tensor as output.
- Usage in Deep Learning: In deep learning, tensors are fundamental for representing data, such as images (as multi-dimensional arrays), text, and numerical values. They are used to perform computations in neural networks, like matrix multiplications and other operations. Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch heavily rely on tensors for data storage and computation in machine learning models.
- Examples:
- Scalar: A single number (e.g., temperature, mass).
- Vector: A one-dimensional array of numbers (e.g., position in space, velocity).
- Matrix: A two-dimensional array of numbers (e.g., a grid of pixels, a transformation matrix).
- Higher-dimensional tensors: Can represent complex data like video frames, 3D images, or even more abstract data structures.
- Key Properties:
- Multilinear: Tensors exhibit linearity in each of their arguments, meaning that they behave predictably when combined with other tensors or vectors.
- Transformation properties: Tensors have specific rules for how their components change when transforming between different coordinate systems.
